HOUR Function Examples – Excel, VBA, & Google Sheets
Download the example workbook
This tutorial demonstrates how to use the Excel HOUR Function in Excel to get the hour of time.
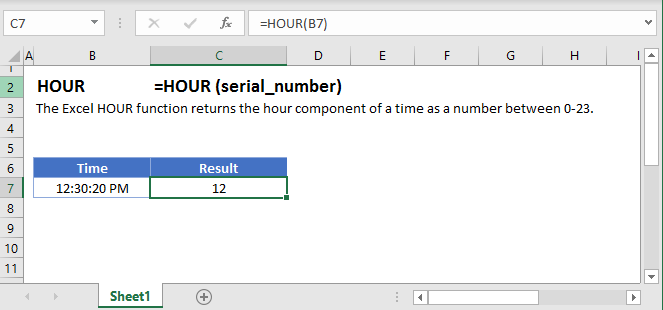
HOUR Function Overview:
The HOUR Function Returns the hour as a number (0-23).
To use the HOUR Excel Worksheet Function, Select cell and Type:
![]()
(Notice how the formula input appear)
HOUR Function syntax and Inputs:
=HOUR(serial_number)serial_number – The time, represented as a fraction of the day or entered as time surrounded by quotations (“s”). Example: You can not enter 8:00:00 pm directly into the cell. Instead you would need to use the corresponding fraction of the day: .3333 or the time surrounded by quorations: “8:00:00 pm”. Alternatively, you can reference a cell with the time entered. Excel automatically converts times stored in cells into a fractional number (unless the time is stored as text).
HOUR Examples
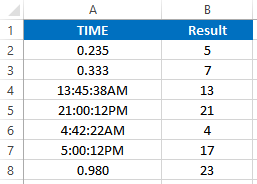
The HOUR Function returns the hour number of a time:
=HOUR(B4)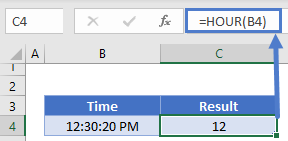
HOUR and TIME Functions
Using the TIME and HOUR Functions you can create a new time with the hour number from the original time:
=TIME(HOUR(B4),10,10)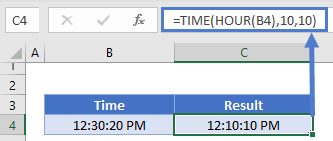
HOUR in Google Sheets
The HOUR Function works exactly the same in Google Sheets as in Excel:
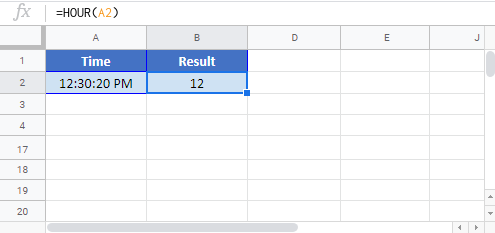
HOUR Examples in VBA
You can also use the HOUR function in VBA. Type:
application.worksheetfunction.hour(serial_number)
Executing the following VBA statements
Range("B2") = Hour(Range("A2"))
Range("B3") = Hour(Range("A3"))
Range("B4") = Hour(Range("A4"))
Range("B5") = Hour(Range("A5"))
Range("B6") = Hour(Range("A6"))
Range("B7") = Hour(Range("A7"))
Range("B8") = Hour(Range("A8"))will produce the following results
For the function arguments (serial_number, etc.), you can either enter them directly into the function, or define variables to use instead.