How to Clean Up Data in Excel & Google Sheets
This tutorial demonstrates how to clean up data in Excel and Google Sheets.
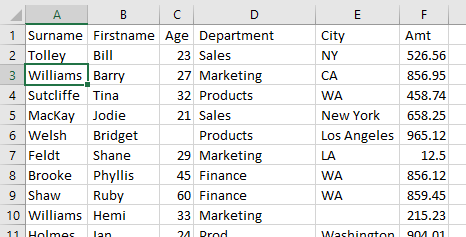
Excel is, for all intents and purposes, a flat-file database; it holds data organized logically into rows and columns. Good, clean data is essential in most of the functionality you need from Excel. There are often issues, however, with data that can cause numerous problems such as extra spaces, blank cells, rows, or columns between data, commas in incorrect places, spelling mistakes, numbers stored as text, etc. This tutorial shows how to clean up data in Excel.
Import Data Into Excel
In some instances, you’ll be entering data directly into Excel, and you can check for accuracy as you go. See How to Create a Searchable Database for tips and instructions.
However, you can also import large amounts of data from external sources such as TXT files or CSV files. This is a convenient and versatile capability of Excel, but imported data can often have entry and import errors you need to remove or repair to ensure the imported data set is accurate and aligns with your needs. Or it might need to be altered a little to use differently from when it was originally set up.
Consider the following TXT file:
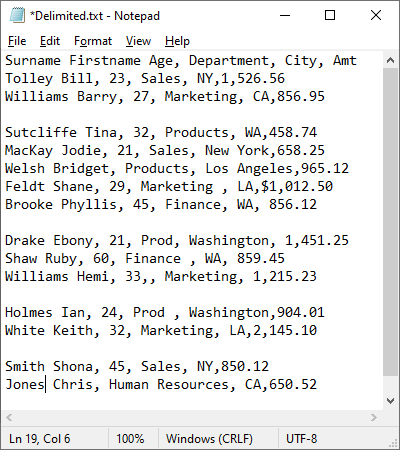
At a glance, the data looks good, so you import it into Excel using Get Data (Power Query).
- In the Ribbon, select Data > From Text / CSV and select the file.
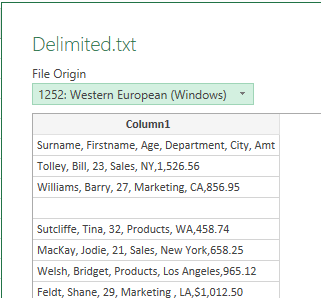
- Because it is a TXT file, it all appears in one column. You can import this and then use the Text to Columns Wizard to separate the data.
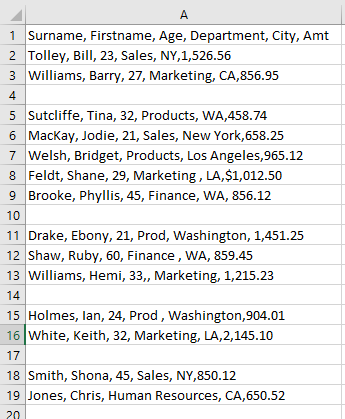
OR
Change the file extension to CSV rather than TXT before you import it. This enables Excel to recognize that it is separated by commas, and it automatically divides the text into columns.
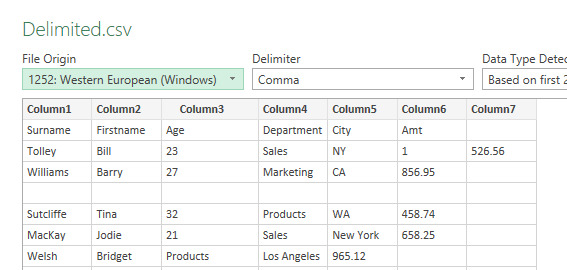
- Once you have imported the file, you need to clean up the data. It comes in formatted as a table.
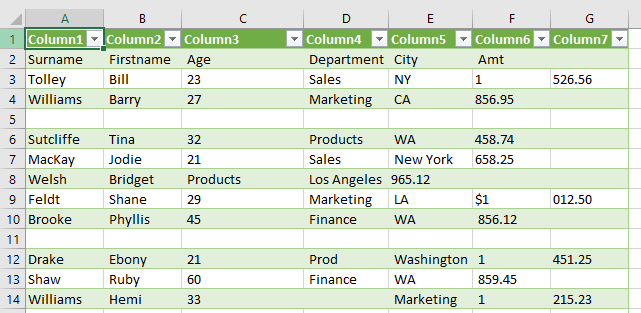
- To remove all formatting, first convert the table to a range.
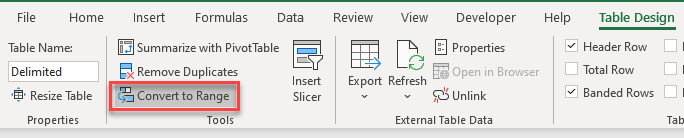
Click anywhere in the table and then, in the Ribbon, select Table Design > Tools > Convert to Range.
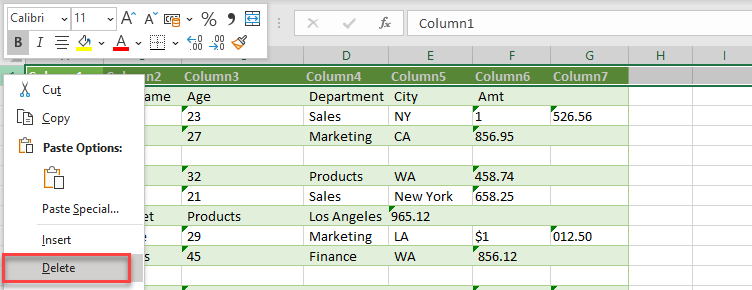
- Then, to remove the top row, select the top row, and then right-click and select Delete.
- Finally, to remove all formatting, select an unformatted blank cell in the worksheet and then, in the Ribbon, select Home > Clipboard > Format Painter.
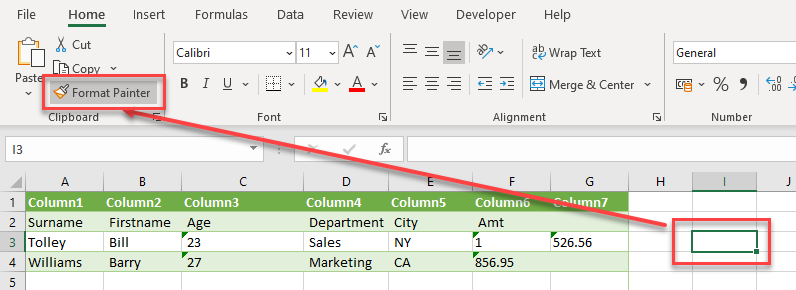
- Then click in the Select All box at the intersection of the row and column headers.
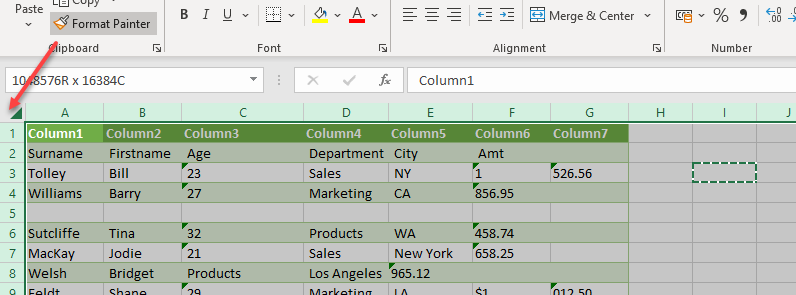
All formatting is removed from the data.
More About Importing Data
- Convert a CSV File to XLSX
- Convert a Spreadsheet to a Delimited Text File
- Import a Word Document
- Import an HTML Table
- Open a Text (.txt) File
- What is the Difference Between CSV Files and Excel Files?
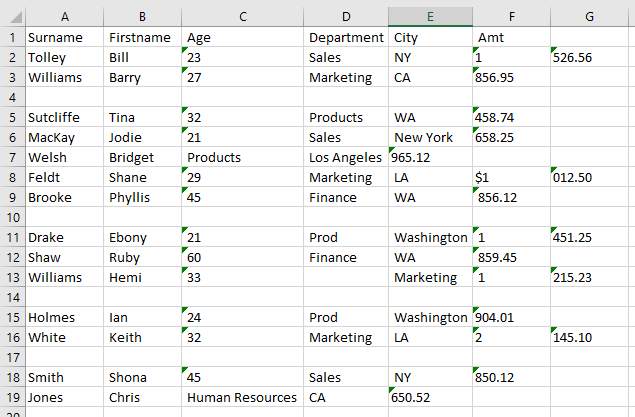
Move Data to Correct Columns
Data may come in but end up in incorrect columns, such as in Row 19 above where the data in Column C should be in Column D. Much of the time it requires manual cleaning – actually moving the data from Column C to Column D manually. On other occasions it may require splitting data where all the data has come in to one column but should in fact be separated.
Combine Two Columns
If a column has been separated due to the data having a comma within the field itself, you need to combine the two columns together.
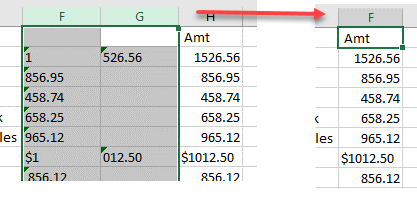
- In the data imported above, the amount field contained a comma when the number was greater than a thousand. You can use a formula with an ampersand to combine these figures.

- As this is now a calculated field, you can copy it down to the rest of the data.
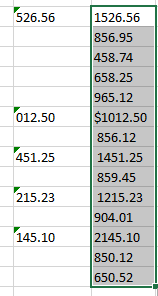
- You can then copy and paste values to change the data from a calculated field back into text.
Now, move the heading (Amt) to the new column and delete the two columns to the left of it.
Spell Check Data
Spelling mistakes can definately come into Excel with imported data. A good idea is to spell check the data once it is imported.
In the Ribbon, select Review > Proofing > Spelling.
Select the correct word from Suggestions, and then click Change.
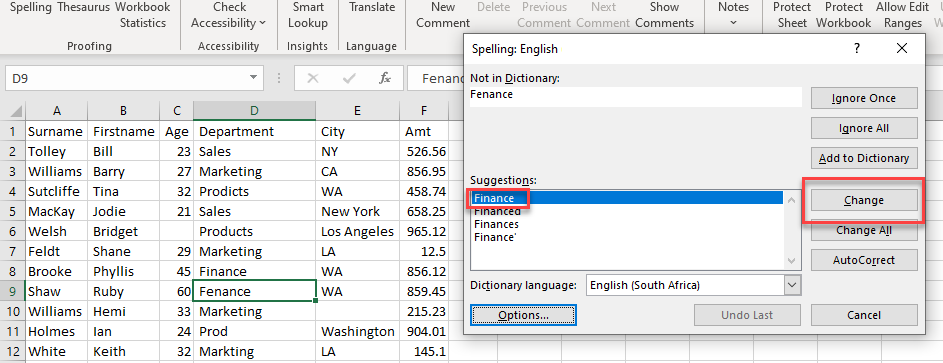
You can Ignore a word if the spelling is in fact correct but not recognised by Excel. You can also add any words to the Dictionary so that they do not come up as spelling errors in future.
Once you have gone through all the data and corrected the mistakes, a message box will pop up.
Remove Blank Rows
Blank rows are a nightmare in Excel data. We can manually delete the blank rows by selecting the first blank row, and then in the Ribbon, select Home > Cells > Delete Sheet Rows.
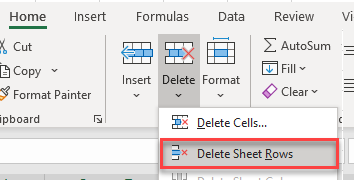
This deletes the selected row. To repeat this, you can select the next row and then press F4 on the keyboard. F4 in Excel repeats the action you have just done and is a pretty efficient way to go down data and delete the rows on condition that you do not have too many rows!
Alternatively, to delete blank rows from the data all at once, follow the instructions here.
More About Keeping Columns and Rows Consistent
- Copy Column Widths
- Copy Row Height
- Unmerge Cells
- Filter Merged Cells
- Make All Rows and Columns the Same Height and Width
- Resize Multiple Rows or Columns at Once
- Resize Cells to Default Row Height
Remove Duplicate Rows
You may find that data has been imported into your file that has some rows that are identical to other rows. In these instances, you may with to Remove Duplicate Rows.
Click in your data and then, in the Ribbon, select Data > Data Tools > Remove Duplicates.
The entire table of data will be selected. You can then select which columns in your data to check for duplicates. As we want to check for duplicate rows, we will leave all the columns selected.
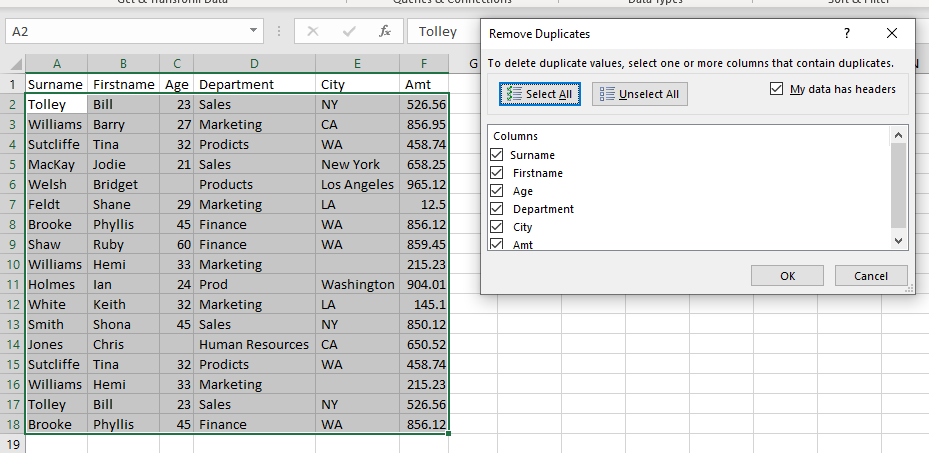
Click OK to remove the duplicate rows.
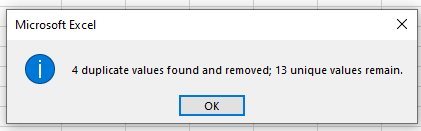
More About Duplicates
- Clear Duplicate Cells
- Merge Lists Without Duplicates
- Remove Unique Values
- Filter Duplicate Values
- Removing Duplicate Values in Excel with VBA
Change Text to Numbers
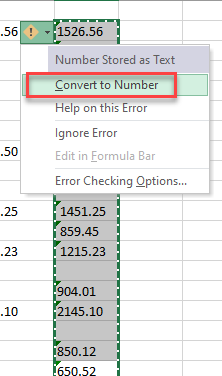
Numbers brought in as text need to be converted to numbers in order to be used in calculations.
To convert the text to numbers, you can highlight the text, click the yellow exclamation mark icon, and choose Convert to Number.
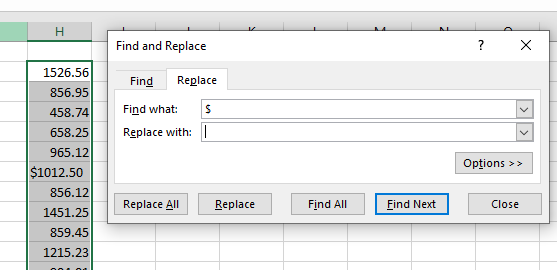
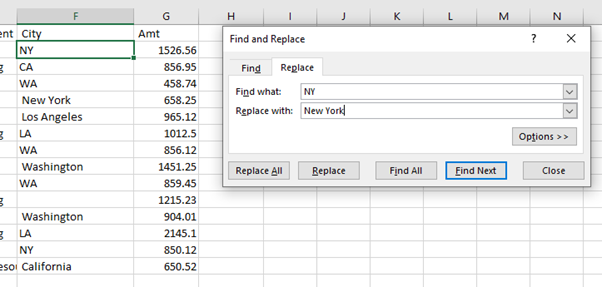
Search and Replace Text
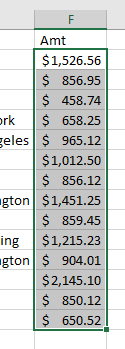
- You can use Find and Replace to remove characters you do not require in the text, for example the dollar sign, which prevents the number from being recognized as Excel as a number.
Then, to show the dollar sign, you can format the column with the currency format.
- In the Ribbon, go to Home > Number and then select Currency.
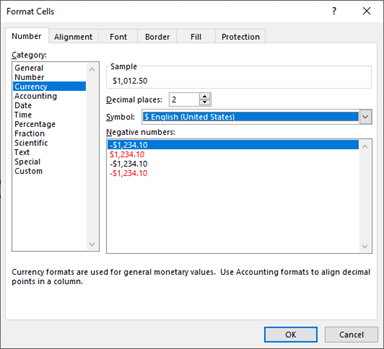
- Click OK to apply the selected currency to the data.
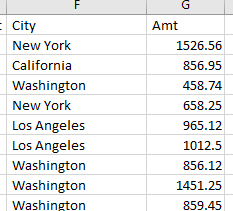
You can also use Find and Replace to replace inconsistent text and make fields ready for analysis.
Repeat as often as necessary.
Remove Trailing Spaces
You may find that data coming in from external sources (especially from external databases) has trailing spaces contained within the cell. While these may not seem to be a huge problem, they can affect sorting or calculations.
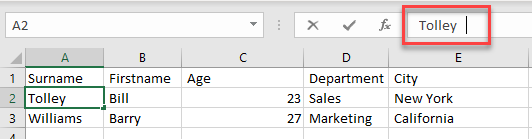
To remove the trailing spaces, use the TRIM Function.
- Insert a new column to the right of the data.
- In the cell next to the text to be trimmed, type the following formula:
=TRIM(A2)
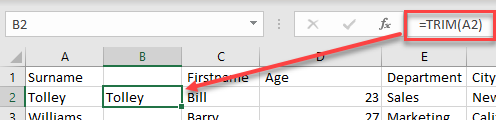
- Copy the formula down to the rest of the data.
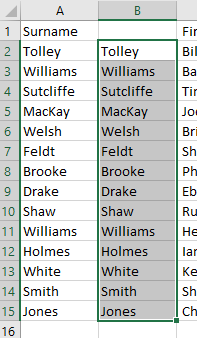
- Copy and paste the data back as values. This removes the trailing spaces.
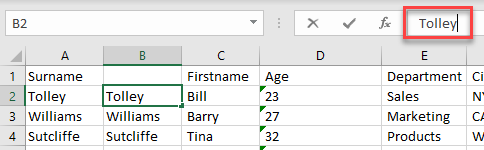
- You can then move the heading (Surname) to cell B1 and delete Column A.
Format Cells
Once the data is in good shape, you’ll probably want to add formatting so it’s easier to read. Our How To page has plenty of tutorials for applying formatting. Here are a few you may find helpful:
- Limit Decimal Places
- Hide Overflow Text in a Cell
- Add Units to Numbers
- Stop Changing Numbers to Dates
- Apply and Change Themes
- Make Cells Bigger to Fit Text
- Automatic Formatting
Clean Up Data in Google Sheets
Import Data Into Google Sheets
You can import data into Google Sheets like you do into Excel.
- Open a Google Sheet, and in the Menu, select File > Import.
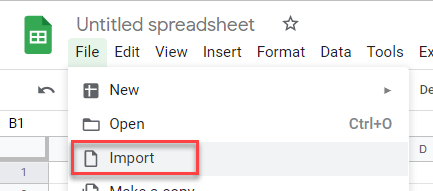
- Select Upload and then select a file from your device.
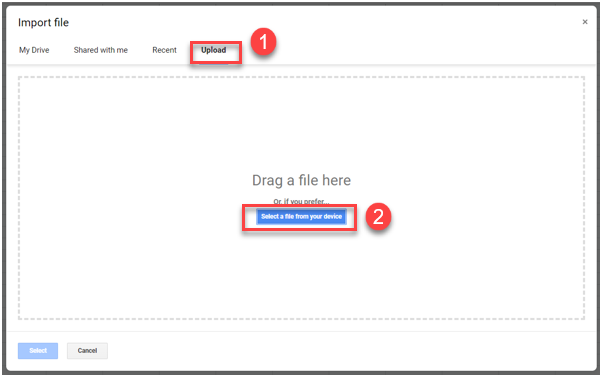
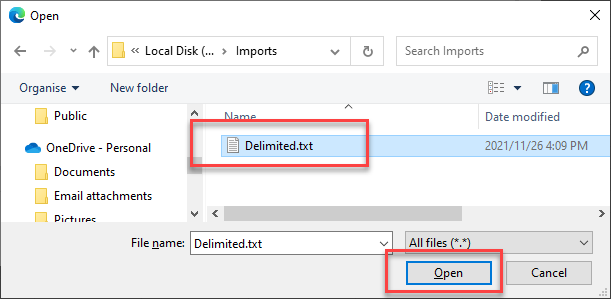
- Select the file you wish to import, then click Open.
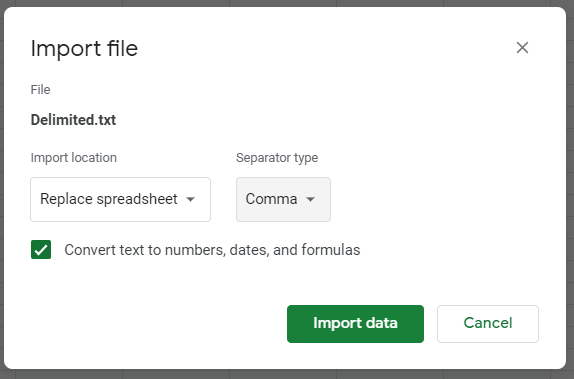
- Amend the Import Location and Separator time as required, and then click Import Data.
The data is now imported into Google Sheets.
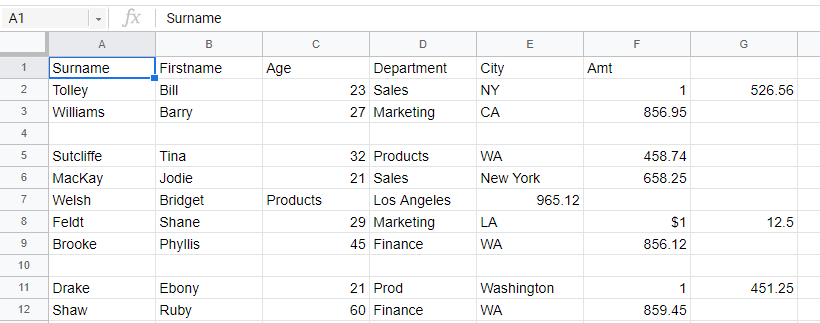
Clean Up Imported Data
Cleaning up data in Google Sheets is similar to cleaning up data in Excel. Google has a built-in clean up
- Data that comes into the wrong column can be moved manually by selecting the data and dragging it across to the correct column.

OR
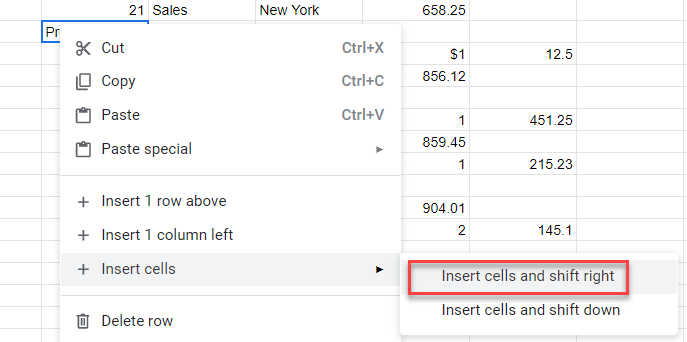
Right-click on the cell to move across, and then, select +Insert cells > Insert cells and shift right.
- As in Excel, you can use a formula to combine to columns.
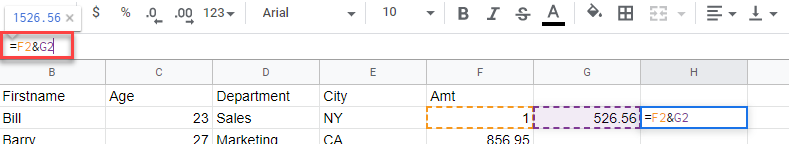
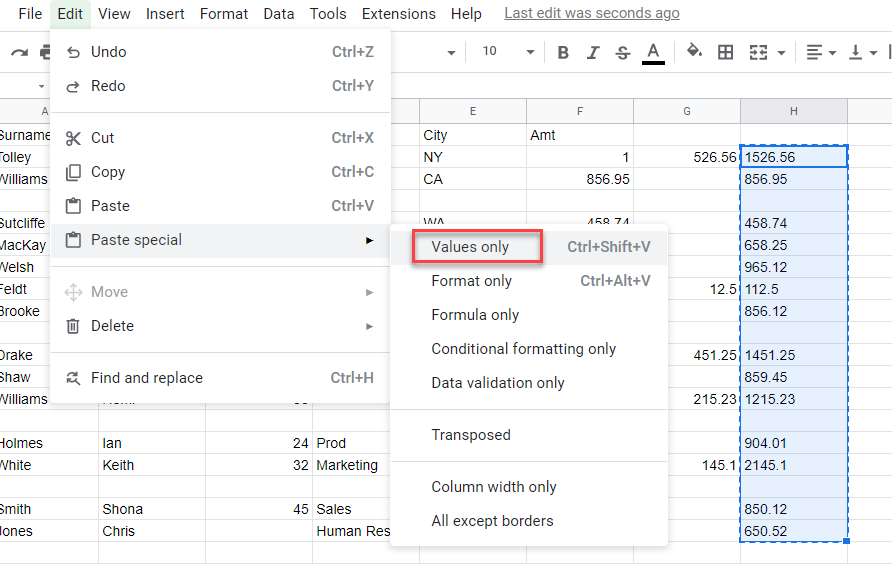
- Drag this formula down, then use Paste Special to replace the formulas with values.
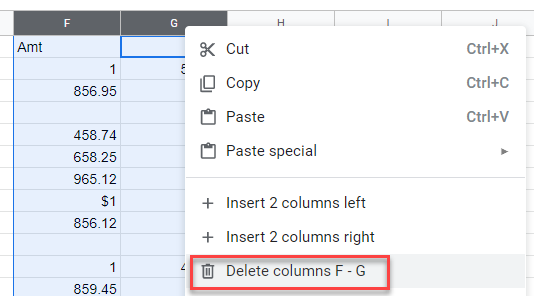
- Once you have done that, you can select the two original columns (in this case Columns F and G), and right-click on the column header to delete the columns.
- You can use the Google Sheets Find and Replace feature to find text and replace it with other text.
In the Menu, select Edit > Find and replace.
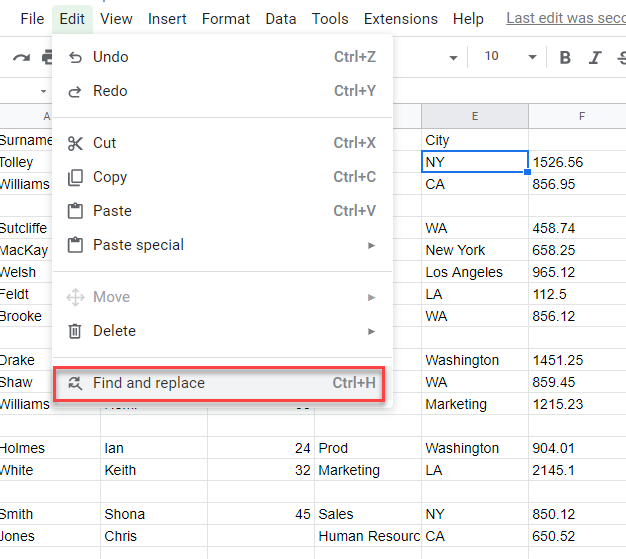
- Type in the text you wish to find, and the text you wish to replace it with, and then click Replace all.
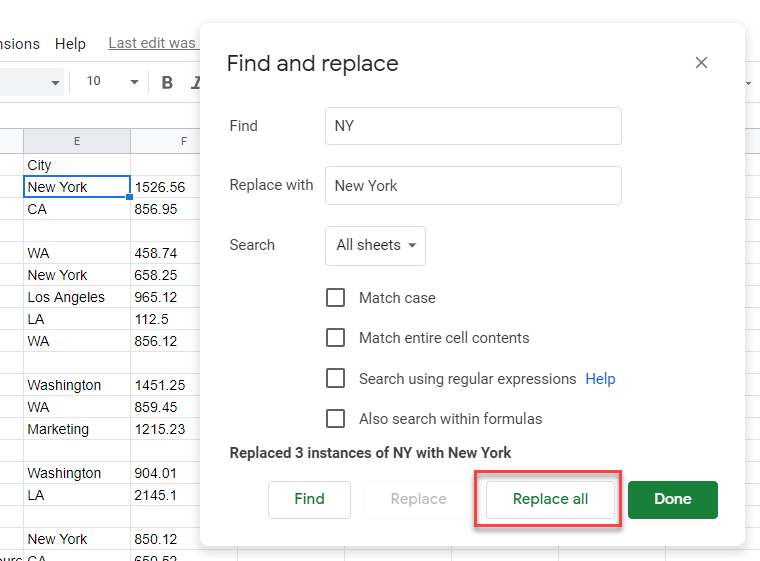
- You can repeat this as often as necessary. Click Done to exit Find and Replace.
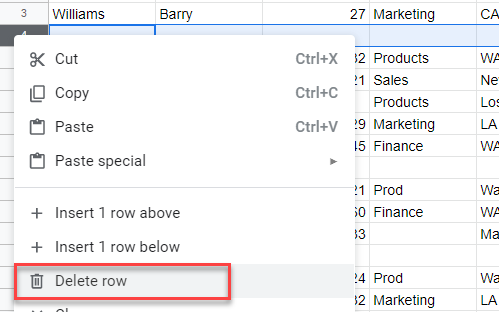
- To remove a single blank row in the data, you can right-click on the row header, and select Delete row.
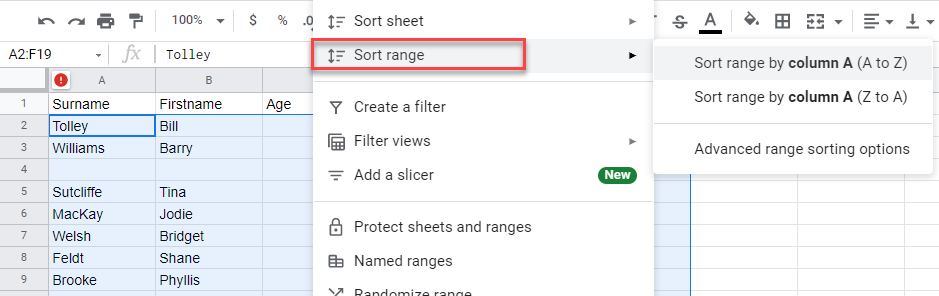
- To remove all the blank rows in the data, you can select the data, and then, in the Menu, select Data > Sort range > Sort range by column A (Z to A).
When you select the data to sort, make sure you exclude the column headers from your selection.
This moves all the blank rows to the bottom of the data, in effect, removing them from the data.
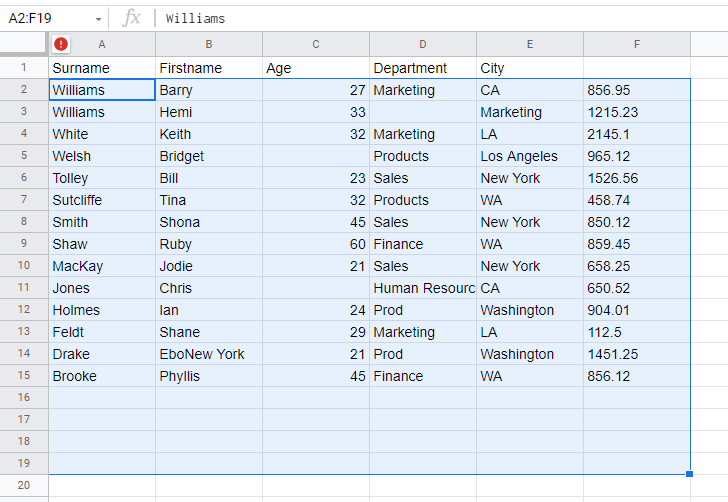
- To remove trailing spaces from the data, select Data > Data cleanup > Trim whitespace.
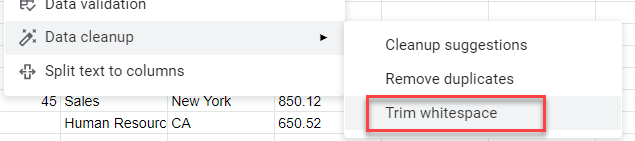
This removes any extra spaces at the end of any of the data.
Google’s Smart Cleanup Feature
Optionally, before you start cleaning the data, you can ask Google for cleanup suggestions based on the imported data.
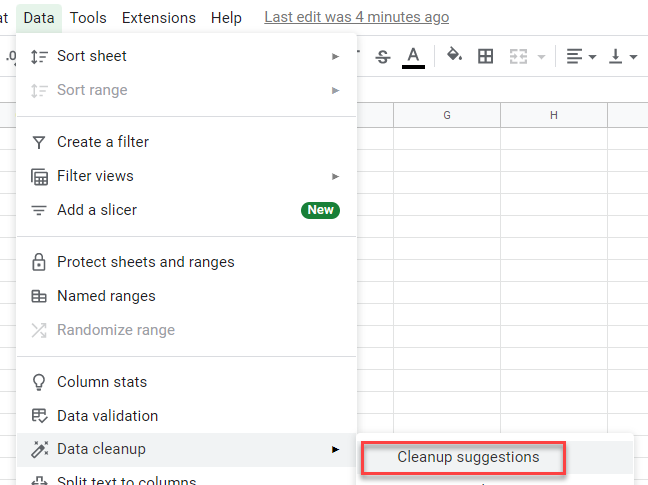
- In the Menu, select Data > Data cleanup > Cleanup suggestions.
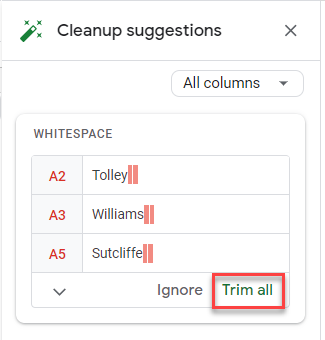
- If Google has any cleanup suggestions, they appear in the right-hand task pane in your Google sheet. In the example below, it has found whitespaces at the end of some words.
Click Trim all to remove the spaces.
You could also use this feature once you have completed cleaning the data to check for anything you may have missed. Don’t let this be your only check, though! It’s still important to review the data with your specific needs in mind.